What is an Object
- Objects group together a set of variables and functions to create a model of a something you would recognize from the real world.
- In an object, variables and functions take on new names.
- a variable in an object, it is called a property.
- a function in an object, it is called a method.
How to Create An Object??
- Literal Notation is the popular way to create objects in Javascript
- Example :

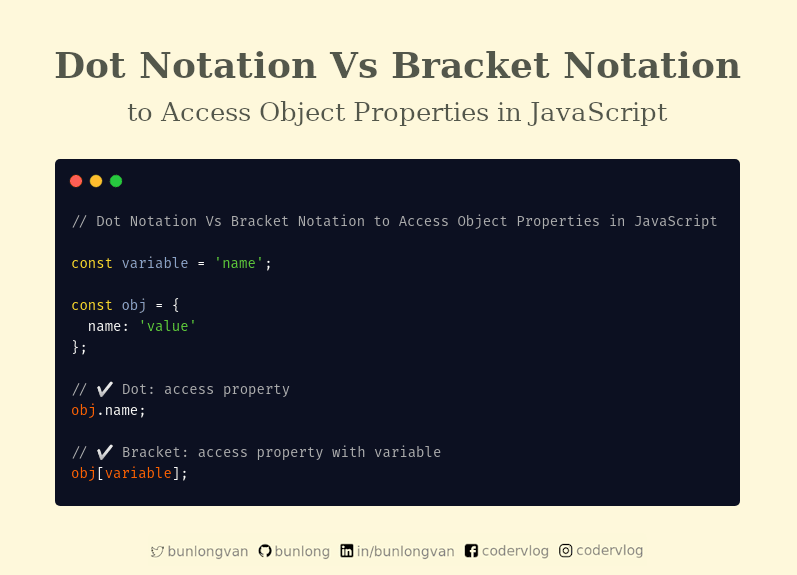
How to Accesse An Object??
- Dot notation is used to access object properties and methods
- bracket notation is used to access object properties
Document Object Model (DOM)
- The Document Object Model (DOM) specifies how browsers should create a model of an HTML page and how JavaScript can access and update the contents of a web page while it is in the browser window
- The DOM specifies the way in which the browser should structure this model using a DOM tree.

What is the DOM Queries??
DOM Queries are the methods that find elements in DOM tree.
-
There are 5 ways in which you can select elements in a DOM using selectors.
-
1- getElementsByTagName()
- This method returns all the elements that matches the specified Tag name.
- document.getElementsByTagName(‘h1’) returns a collection of items matching the tag name h1.
- document.getElementsByTagName(‘li’) returns a list of 5 elements as we have five li tags in our page.
- And any individual element can be selected by using it’s index such as document.getElementsByTagName(‘li’)[ 0 ]
-
2- getElementsByClassName()
- This selector is very similar to getElementsByTagName except the selection is based on Class name and not Tag name. You can see some examples from the image above.
-
3- getElementById()
- this selector returns only the first matched element while ignoring the remaining.
-
4- querySelector()
- This one returns the first element that matches the specified CSS selector in the document.
- document.querySelector(‘li’) returns the first element that matches the CSS selector li. Remaining elements are ignored.
- As you can see, we can use all kinds of CSS selectors within the querySelector method that we will use in a normal CSS file.
-
5- querySelectorAll()
- This method returns all the elements that match the specified CSS selector in the document.
- document.querySelectorAll(‘.heading’) returns a list of all elements that matches the specified CSS selector. Since we have only one element under the class name .heading, the list contains one element. And it can be accessed by it’s index.

-
Nodelist
- NodeList is DOM query that returns more than one element.
- getElementsByTagName()
- getElementsByClassName()
- querySelectorAll()
-
How to select an element from NodeList
-
1- item()
-
The item() method returns a node at the specified index in a NodeList object.
-
The nodes are sorted as they appear in the source code, and the index starts at 0.
- A Node object’s collection of child nodes is an example of a NodeList object.
var div = document.getElementById(“myDIV”); var nodelist = div.getElementsByClassName(“child”); var i; for (i = 0; i < nodelist.length; i++) { nodelist[i].style.backgroundColor = “red”;}
-
2- classname
- The className property sets or returns the class name of an element (the value of an element’s class attribute).
- Set the class for a < div > element with id=”myDIV”: document.getElementById(“myDIV”).className = “mystyle”;
-

Traversing the DOM.
- When you have an element node, you can select another element in relation to it using these five properties. This is known as traversing the DOM.


Accessing and changing a text node
-
1- node.textcontent
-
Return the text content of a node:
node.textContent
-
Set the text content of a node:
node.textContent = text

-
2- innertext
- The innerText property sets or returns the text content of the specified node, and all its descendants. If you set the innerText property, any child nodes are removed and replaced by a single Text node containing the specified string.

Adding and Removing Html Content
-
1- innerHtml
The innerHTML property sets or returns the HTML content (inner HTML) of an element.

-
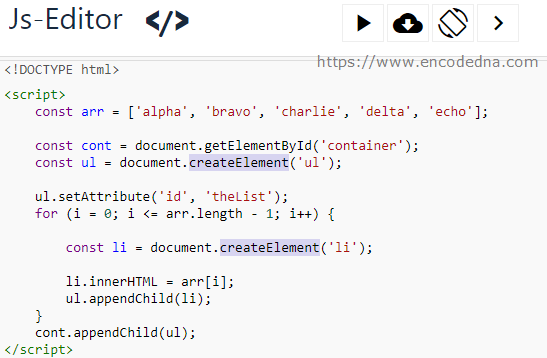
DOM manipulation
offers another technique to add new content to a page (rather than innerHTML). It involves three steps:
- 1- createEl ement ()
- 2- createTextNode()
- 3- appendChild()
How can you access and change node attribute
- This Process achives by getattribute() method
- The getAttribute() method returns the value of the attribute with the specified name, of an element.

How to specify attribute to an element, and give it the specified value?
- This Process achives by setattribute() method
How to remove attribute to an element?
- This Process achives by removeattribute() method
